
MYNX CONTROL Vascular Closure Device
The innovative design and predictable deployment of MYNX CONTROL® Vascular Closure Device (VCD) delivers outstanding performance and control for consistently secure arterial closures.

Close with confidence. Leave nothing behind.
MYNX CONTROL VCD integrates dual-mode active sealing and reabsorbability with a next-generation delivery system to maximize predictability, safety, and ease of use in 5F, 6F, and 7F sizes.
Secure extravascular closure in a wide range of clinical scenarios.
With exceptional versatility, MYNX CONTROL VCD offers dependable closure with nothing left behind*—even in cases where using a different vascular closure device might be unsuitable.

Safe for bifurcations2†
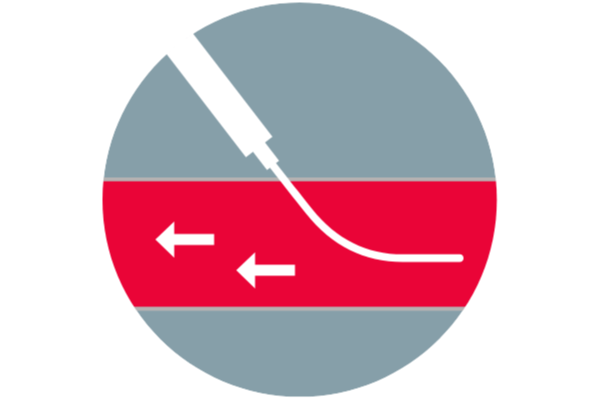

Useful on antegrade punctures3
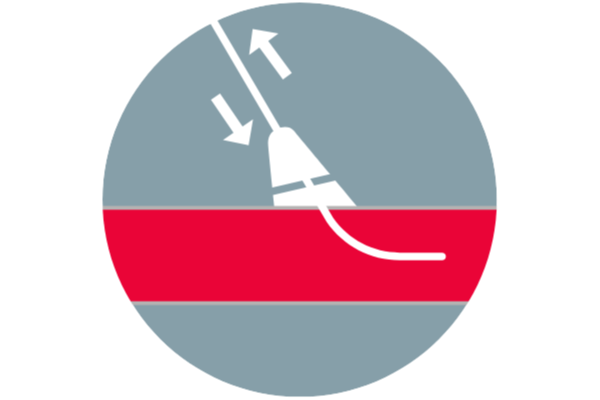

No footplates, sutures, or metal implants to impede reaccess
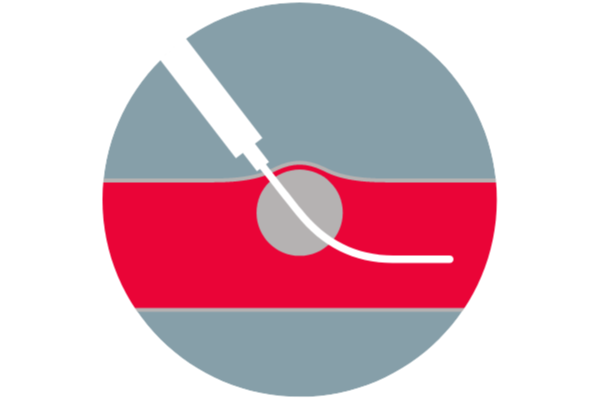
Balloon visualization verifies position
† Confirm vessel size is ≥ 5 mm
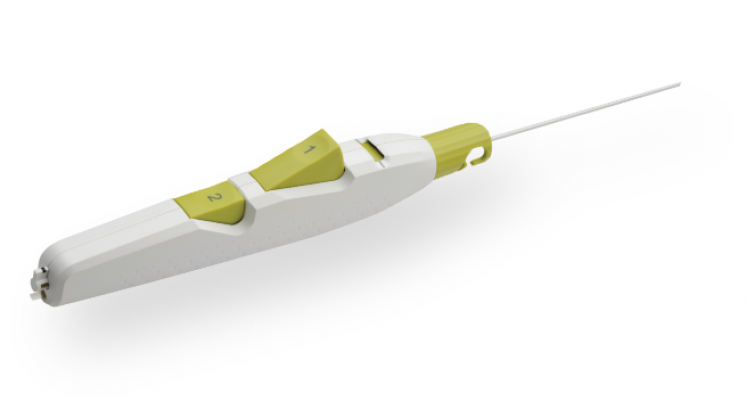

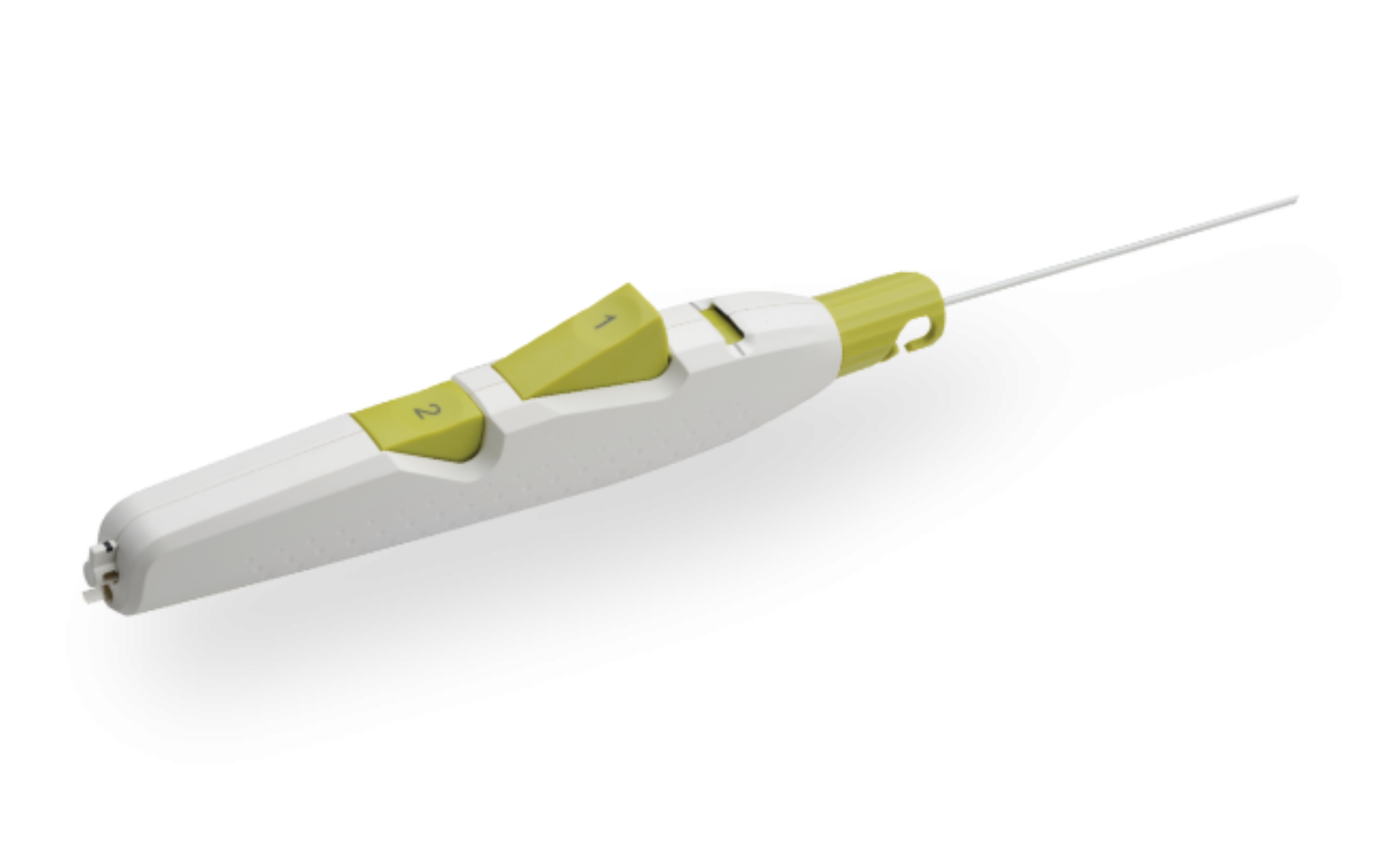
Product Highlights
Sheath Catch
Compatible with procedural sheath limited the need for sheath exchanges.
Button #1
Deploys and compresses the sealant.
Tension Indicator
Provides visual confirmation of device position for proper sealant deployment.
Button #2
One-step balloon withdrawal.
Ergonomic Handle
Facilitates ease of use for predictable deployment.
The Science of Active Extravascular Sealing
MYNX CONTROL VCD consists of two configurations of polyethylene glycol (PEG), for durable hemostasis.
- SAFE
No foreign-body reaction or scar tissue formation1 - SYNTHETIC
Non-thrombogenic1 - HYDROLYTIC DEGRADATION
Fully resorbs through hydrolysis—no enzymatic breakdown1 - MYNX GRIP TIP
Activated by body temperature and pH Interlocks with contours of the vessel by actively attaching to the artery, for secure mechanical closure - MYNX® SEALANT COLUMN
Expands to 3-4 times its original size on contact with blood and subcutaneous fluids, creating a matrix structure for clot formation

Safety by the Numbers.
MYNX CONTROL VCD has been clinically proven to reduce surgical complications, expedite recovery, shorten hospital stays, and increase patient comfort.2-7‡
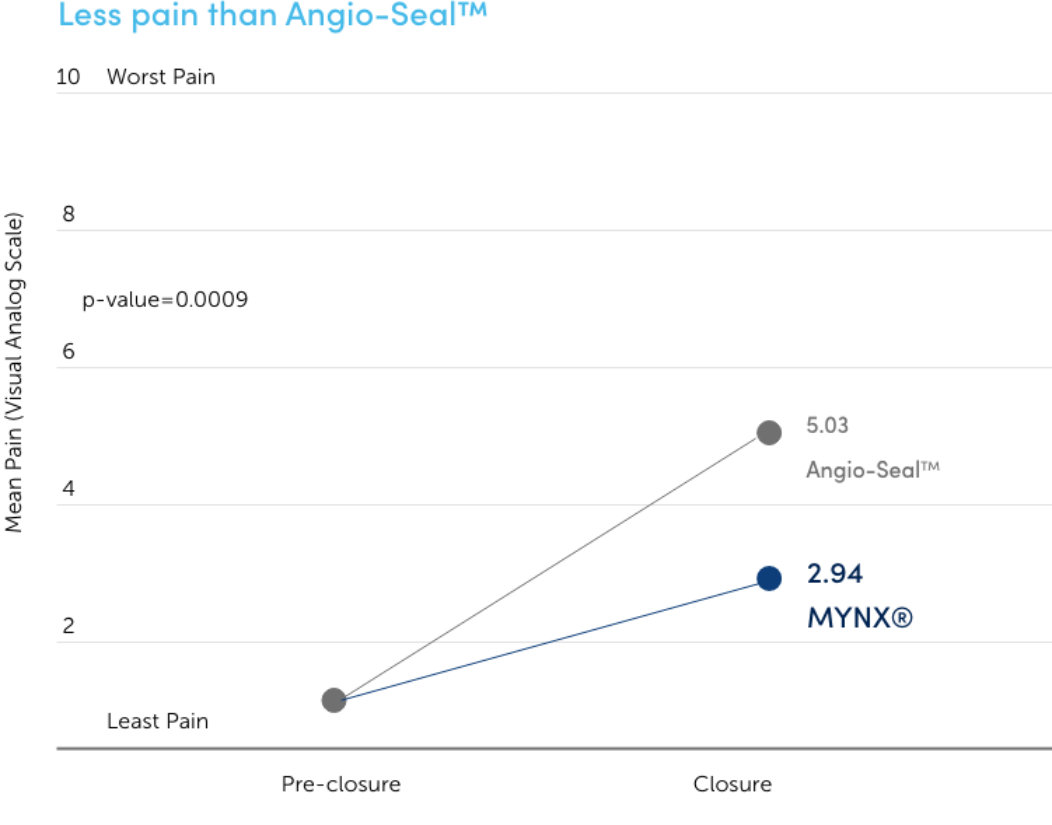
Increased Patient Comfort
In a blinded, randomized clinical study, pain at closure and pain increase from baseline to close were significantly lower for MYNX CONTROL VCD than Angio-Seal™ vascular closure device.7
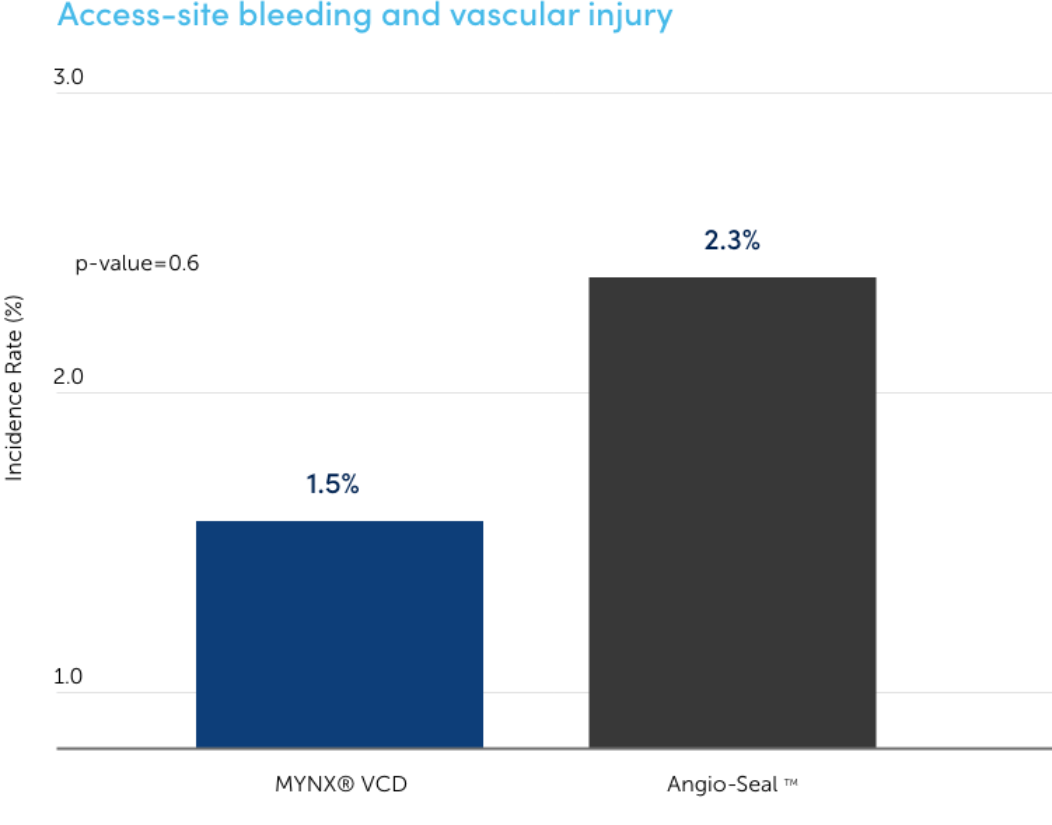
Access-site bleeding and vascular injury
Reduced incident rate In a blinded, randomized clinical study, there was a significantly reduced incident rate for MYNX Portfolio of products than Angio-Seal VCD.
Ordering Information
| Product | Size |
Order No. |
Quantity |
Components |
| MYNX CONTROL® Vascular Closure Device | 5F |
MX5060 |
10 ea/box |
1x MYNX CONTROL® VCD including balloon catheter and integrated polyethylene glycol extravascular sealant 1x 10 ml locking syringe |
| MYNX CONTROL® Vascular Closure Device | 6F / 7F |
MX6760 |
10 ea/box |
1x MYNX CONTROL® VCD including balloon catheter and integrated polyethylene glycol extravascular sealant 1x 10 ml locking syringe |
| Product | Size |
Order No. |
Quantity |
Components |
| AVANTI® + Sheath Introducer 11 cm | 5F |
402-605X |
5 ea/box |
1x Mid-length 11cm Cannula 1x Mini-Guidewire |
| AVANTI® + Sheath Introducer 11 cm | 6F |
402-606X |
5 ea/box |
1x Mid-length 11cm Cannula 1x Mini-Guidewire |
| AVANTI® + Sheath Introducer 11 cm | 7F |
402-607X |
5 ea/box |
1x Mid-length 11cm Cannula 1x Mini-Guidewire |
References
1. Scheinert D, Sievert H, Turco MA, et al. The safety and efficacy of an extravascular, water‐soluble sealant for vascular closure: Initial clinical results for Mynx. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent. 2007 Oct;70:627-633.
2 MYNX CONTROL Vascular Closure Device Instructions for Use.
3 Pruski MJ Jr, Blachut AM, Konkolewska M, et al. MynxGrip for closure of antegrade puncture after peripheral interventions with same-day discharge. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2017 Feb;51(2):67-71.
4 Baker NC, Escarcega RO, Lipinski MJ, et al. Active versus passive anchoring vascular closure devices following percutaneous coronary intervention: a safety and efficacy comparative analysis. J Interv Cardiol. 2016 Feb; 29(1): 108-112.
5 Hutchings D, Hayat A, Karunakaran A, Malik N. Success, safety, and efficacy of the Mynx femoral closure device in a real-world cohort: single-center experience. J Invasive Cardiol. 2016 Mar;28(3):104-108.
6 Noor S, Meyers S, Curl R. Successful reduction of surgeries secondary to arterial access site complications: a retrospective review at a single center with an extravascular closure device. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2010 Jul;44(5):345-349.
7 Fargen KM, Hoh BL, Mocco J. A prospective randomized single-blind trial of patient comfort following vessel closure: extravascular synthetic sealant closure provides less pain than a self-tightening suture vascular compression device. J NeuroInterv Surg. 2011 Sep; 3(3): 219-223.
† Confirm vessel size is ≥ 5 mm
‡Time to discharge eligibility as compared to manual compression. MATRIX Clinical Trial (IDE# G030182)
IFU
Please refer to the Instructions for Use for complete information, including indications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events.
Customer Service and Ordering Information
In the United States, email us your question or order, or call us at 800.327.7714.

